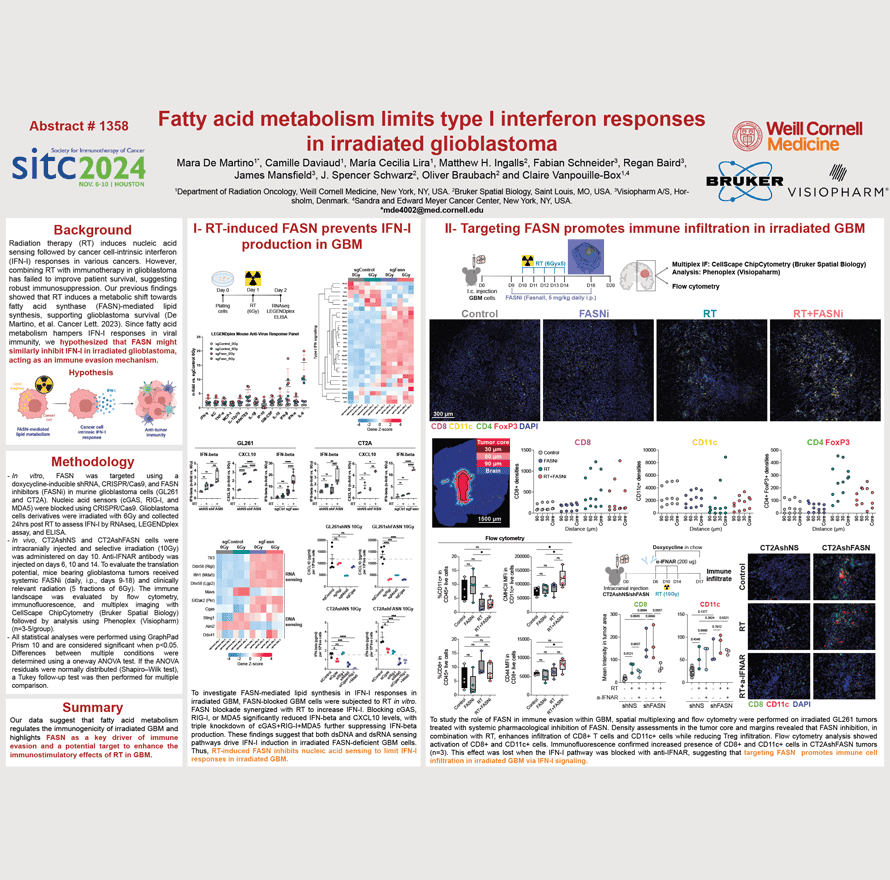
Radiation therapy (RT) induces nucleic acid sensing followed by cancer cell-intrinsic interferon (IFN-I) responses in various cancers. However, combining RT with immunotherapy in glioblastoma has failed to improve patient survival, suggesting robust immunosuppression. Our previous findings showed that RT induces a metabolic shift towards fatty acid synthase (FASN)-mediated lipid synthesis, supporting glioblastoma survival (De Martino, et al. Cancer Lett. 2023). Since fatty acid metabolism hampers IFN-I responses in viral immunity, we hypothesized that FASN might similarly inhibit IFN-I in irradiated glioblastoma, acting as an immune evasion mechanism.
Mara De Martino1, Camille Daviaud1, María Cecilia Lira1, Matthew H. Ingalls2, Fabian Schneider3, Regan Baird3, James Mansfield3, J. Spencer Schwarz2, Oliver Braubach2 and Claire Vanpouille-Box1,4
- Department of Radiation Oncology, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, USA
- Bruker Spatial Biology, Saint Louis, MO, USA
- Visiopharm A/S, Horsholm, Denmark
- Sandra and Edward Meyer Cancer Center, New York, NY, USA
New Views in Spatial Biology: Multiplexed Imaging for Rapid Whole Slide Analysis
Join us for an insightful seminar on the Hyperion XTi™ Imaging System and its pivotal role in advancing spatial biology. This emerging field is transforming our understanding of tissue organization in health and disease, with implications for predicting immune and therapeutic responses, improving drug development strategies, and potentially preventing or curing diseases.
While conventional microscopy techniques use fluorescence to visualize protein or RNA targets in tissue samples, they face challenges due to spectral overlap and tissue autofluorescence. The Hyperion™ XTi overcomes these limitations by utilizing Imaging Mass Cytometry™ (IMC™), a fluorescence-free approach enabling detection of 40+ targets.
IMC has expanded its capabilities with new whole slide imaging modes, which include Preview Mode, Cell Mode and Tissue Mode. These modes facilitate rapid and detailed analysis, supporting automated, continuous imaging of more than 40 large tissue samples (400 mm²) weekly. This significantly accelerates researchers’ ability to gain insights from complex biological samples.
Phenoplex™ software from Visiopharm® complements this hardware by offering a comprehensive workflow for data analysis, including automated ROI selection, phenotyping and spatial analyses of IMC images. This seminar will demonstrate how the multi-modal features of Hyperion XTi, combined with advanced analysis tools from Visiopharm, are revolutionizing our approach to spatial biology and opening new avenues for biological assessment.

James Pemberton, PhD
James holds a PhD in medical biophysics from the University of Toronto, specializing in advanced fluorescence microscopy techniques, cell biology and cell signaling mechanisms. At Standard BioTools, he currently works within product management and collaborates with R&D teams to leverage the multi-plex capabilities of the Hyperion XTi Imaging System. His goal is to drive innovation in spatial biology, enhancing our understanding of complex cellular interactions and tissue architecture in both health and disease.

This white paper presents a detailed analysis using Phenoplex to study a highly multiplexed 30-biomarker assay of colorectal cancer (CRC) tissue, focusing on the spatial distribution of cytotoxic GZMB+ cells within CD8+ T cells and CD56+ NK cells. The study identifies these immune cells and examines their proximity to cytokeratin-expressing epithelial cancer cells. By segmenting the tissue into eight specific regions based on HLA-DR expression, the analysis reveals distinct patterns in immune cell infiltration and proximity, highlighting higher densities of cytotoxic T cells in HLA-DR- regions compared to HLA-DR+ regions. These findings suggest that the immune landscape and spatial relationships in the tumor microenvironment (TME) are crucial for understanding CRC pathology and potentially guiding therapeutic strategies.
The spatial information allows scientists to investigate neighborhoods and distances of specific cell populations to each other to decode the complexity of tissue microenvironments in normal and disease states. Especially in immune oncology the neighborhood composition of tumor and immune cells is important to fully understand cell interactions to develop novel precision diagnostics.
The Phenoplex workflow now includes hypothesis-driven spatial analysis options for cellular proximity counts of neighboring cells and nearest neighbor distance calculations. Using our intuitive workflow, users can define the target cells and interrogate their neighbors within a defined radius.
HOST-Factor: Unveiling pancreatic cancer microenvironment neighborhoods through highplex imaging and spatial profiling
HOST-Factor: Unveiling pancreatic cancer microenvironment neighborhoods through highplex imaging and spatial profiling


Solid tumors’ complexity extends beyond the genetic and functional diversity of cancer cells to include the tumor microenvironment (TME). Understanding the TME’s complexity requires a comprehensive analysis of the composition, functional states, and spatial distribution of its cellular components.
In this session, we will explore the application of basic research discoveries through the Harmonic Output of Stromal Traits (HOST) for the evaluation of the TME. HOST is designed to identify TME cells, while the HOST-Factor quantifies their functional states. The HOST-Factor is a numerical value reflecting the relative contribution of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) to tumor-suppressive or tumor-promoting functions.
Our workflow combines automated high-plex immunofluorescent microscopy with AI-guided image analysis to generate single-cell HOST-Factor values. This approach, applicable to the entire TME or specific regions of interest, provides spatial distribution data and identifies potential tumor-promoting or suppressive neighborhoods.
This talk will highlight the application of Visiopharm’s Phenoplex workflow and its Neighbor Counts module to identify and evaluate HOST+ CAF populations and their spatial distribution. Developed specifically for a pancreatic cancer clinical trial at Fox Chase Cancer Center, this user-friendly pipeline is flexible and useful for assessing diverse stromal compartments in distinct solid tumor cases.

Janusz Franco-Barraza. MD, PhD
Dr. Franco-Barraza obtained his Ph.D. in Molecular Biomedicine in 2010 from CINVESTAV-IPN (Center for Research and Advanced Studies of the National Polytechnic Institute, Mexico). During his postdoctoral work at Fox Chase Cancer Center, he studied integrin-based activation mechanisms used by cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF) within their self-secreted extracellular matrix (ECM), acting as complex entities called CAF units. He focuses on understanding the functional traits of these CAF units and their roles in tumor promotion or suppression.
Utilizing approaches including multiplexed immunofluorescence and artificial intelligence (AI)-driven digital image mining, he is dedicated to understanding the prevalence and interplay of CAF units with other resident cells within the tumor microenvironment. Currently, his research aims to profile the stroma of cancer patients to validate and implement fibroblastic biomarker signatures that could predict treatment responses and disease outcomes.
Multiplex users deserve analysis software designed for multiplex images. Phenoplex is the only complete workflow software for multiplex tissue images, built on Visiopharm’s best-in-class AI, with interactive verification steps throughout. Make new discoveries, compare between cohorts, or reproduce previous results. Phenoplex’s comprehensive workflow lets you rapidly confirm observations, no matter the ‘plex level, so you can move on to the next multiplex experiment.