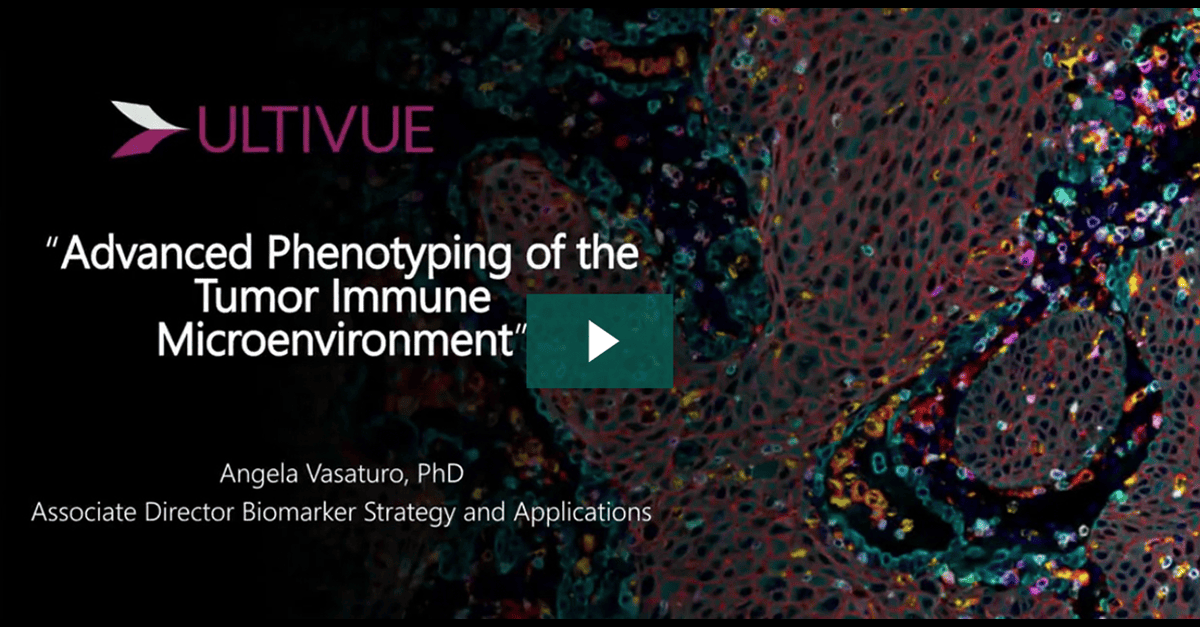
Immunotherapy has transformed the treatment of metastatic and recurrent solid tumors but is challenging in that only a minority of patients respond. Therapies that rely on immune activation, such as checkpoint inhibitors, have been shown to be especially difficult due to the complex and heterogeneous immune escape mechanisms which can develop in each patient. Therefore, development of robust biomarkers coupled with spatial analysis of tissue is key for enabling rational patient selection and the design of precise combination therapies.
The use of multiplex immunohistochemistry/immunofluorescence (mIHC/IF) provides much needed insight into cellular composition, cellular functions, and cell-cell interactions. Importantly, recent studies have used mIHC/IF to explore specific immune cells as part of the tumor immune microenvironment (TME) and found that it is helpful for clinical prognosis and efficacy prediction in patients with cancer.
In this presentation we will show a streamlined unique workflow supporting whole slide imaging of an 8-plex mIF and H&E fusion on a single tissue slide for a comprehensive tissue immunophenotyping analysis.
-
- The utility of a high throughput, high-plex (Immuno-8) staining and mIF assay development for scientists and clinicians
-
- Demonstrate how advanced AI-driven image analysis can be applied to discover cell types, populations and morphological context
-
- Discuss how whole slide image analysis of the tumor microenvironment can provide insight into specific cancer types

Fabian Schneider, PhD, Service Project Lead, Visiopharm
Dr. Fabian Schneider is part of Visiopharm’s R&D and Product Management team, responsible for phenotyping products as well as service projects for custom APP development. Fabian has over 10 years of international experience in cancer biology and immuno-oncology, working in academic research labs, clinical research teams and computational pathology groups in both academia and biopharma. Fabian received his Dr phil. nat. in Cell Biology in 2011 from the Johan Wolfgang Goethe University Frankfurt, Germany.
Angela Vasaturo, PhD
Associate Director, Biomarker Strategy and Applications
Only a small subset of patients with clear cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (ccRCC) respond to immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors. Research has shown that additional mechanisms of inhibition prevent the majority of patients from successful treatment. Recent studies into the inhibitory role of macrophages portend that these cells are associated with lower survival rate in several different cancer types. In this webinar, Immunologist Prof Dr Elfriede Nößner will present her research on specific macrophages in RCC (“ercDCs”) which are associated with poor outcome and their potential as new targets in immune therapy.
Presented as a LabRoots webinar on January 19, 2021.
-
- What is known about the role of macrophages in immuno-oncology in general and in RCC specifically
-
- What are “ercDCs” and how do they interact with T-Cells in RCC?
-
- Which possibilities exist to manipulate the ercDCs?

Dr Elfriede Nößner, Head of Immunoanalytics, Helmholtz Zentrum München, German Research Center for Environmental Health
Dr. Elfriede Noessner is professor at the Ludwig-Maximilians-University of Munich (LMU) in Munich, Germany, and employed by the Helmholtz Zentrum Munich, where she is the Head of Immunoanalytics Research Group. She is board certified in immunology by the German Society of Immunology. She spent 5 years at Stanford University. Her research topics include the biology of HLA proteins and the antigen presentation; the activation, maintenance and control of T cell responses; and the modulation of T and NK cells, as well as dendritic cells and macrophages in tissue milieus, including cancer.
Find out why Dr Rimm’s work suggests that a subset of cells that have lost beta-catenin expression may be associated with non-response. In this seminar recording from USCAP 2020, Dr Rimm explains how you can benefit from exploratory analysis using AI-powered phenotyping.
Learn how his group used Visiopharm AI-based software to help them get meaningful results from next-gen imaging technologies like Fluidigm’s IMC.
-
- Methods of measurement –co-localization, compartmentalization, and measurement vs segmentation and counting
-
- How his lab used tSNE plots to show differences between responders and non-responders to trastuzumab

David Rimm, MD, PhD, Professor of Pathology and Medicine (Oncology); Director of Yale Pathology Tissue Services. Yale School of Medicine
David has authored over 400 peer-reviewed papers and holds eight patents. His research lab group focuses on quantitative pathology using the AQUA® technology invented in his lab, and other quantitative methods, including Visiopharm´s phenotyping module.
His projects relate to predicting response to both targeted and immune- therapy in cancer and standardization of those assays for CLIA labs.