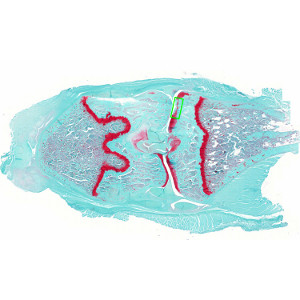
Coronal histological section of rat knee joint, stained with Safranin-O and Fast Green. Analysis box placed at the medial tibia cartilage.
#10027
Surgically-induced knee joint instability in rats by transection of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACLT), partial medial Meniscectomy (pMx) or a combination of both (ACLTpMx), is one of the most commonly used experimental animal models of osteoarthritis (OA), see [1],[2]. It shows very similar anatomical location and histopathological features as the human disease. The model is suitable for studying basic pathophysiological aspects of OA and for the pharmaceutical development of disease-modifying drugs.
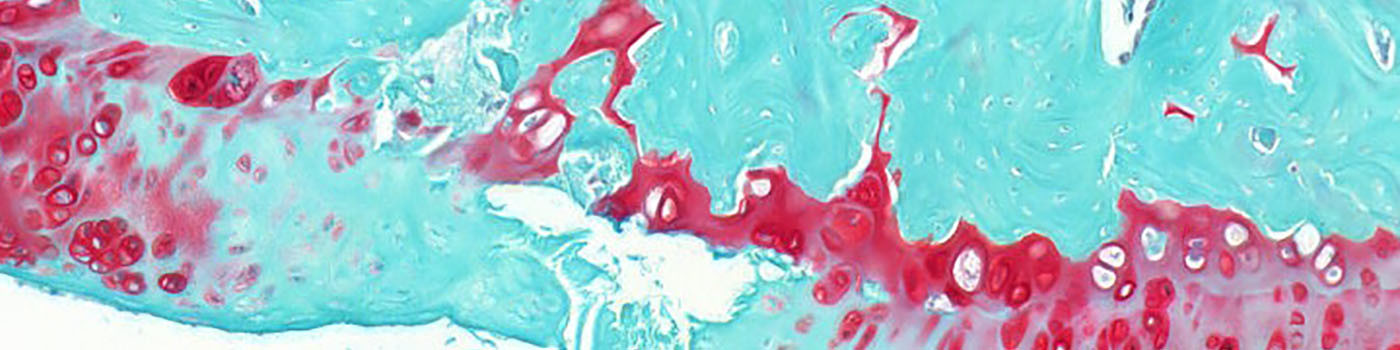
The severity of joint destruction can best be demonstrated in coronal histological sections of the whole knee joint; stained with Safranin-O-Fast Green (or Hematoxilin-Eosin, see related APP no. 10026). The most important histopathological hallmarks are surface fibrillation and erosion of the articular cartilage, decrease in chondrocyte number, loss of proteoglycan staining and a sclerosis (thickening) of the subchondral bone plate.
Traditionally, the evaluation of the severity of joint damage is done by subjective semi-quantitative grading of the different histopathological features using defined scoring systems, see [3]. However, even with ‘blinding’ of the observers and sample randomization, this methodology is prone to bias, suffers from low sensitivity to change and requires considerable experience in histopathology. On the other hand, quantitative digital histomorphometry of cartilage destruction and subchondral bone sclerosis can offer an objective, less time consuming and more sensitive assessment of OA histopathology, see [4].
This APP can be used for quantifying a number of parameters relating to joint damage: Cartilage volume/area, surface fibrillation and proteoglycan loss (intensity measure). The APP has been verified in both age-dependency studies and treatment studies.
Auxiliary APPs
Auxiliary APPs are used for additional process steps, e.g. finding Region of Interest (ROI).
RECALCULATE
The auxiliary APP ‘Aux 01 RECALCULATE’ can be used for recalculation of output values, after manual editing of tissue delineation.
Quantitative Output variables
The output variables obtained from this APP include:
Methods
This APP can be used on virtual slides with several sections on each slide. Initially an Analysis Box with a predefined size is placed manually at the medial tibia cartilage, including potential lesion area and excluding osteophytes.
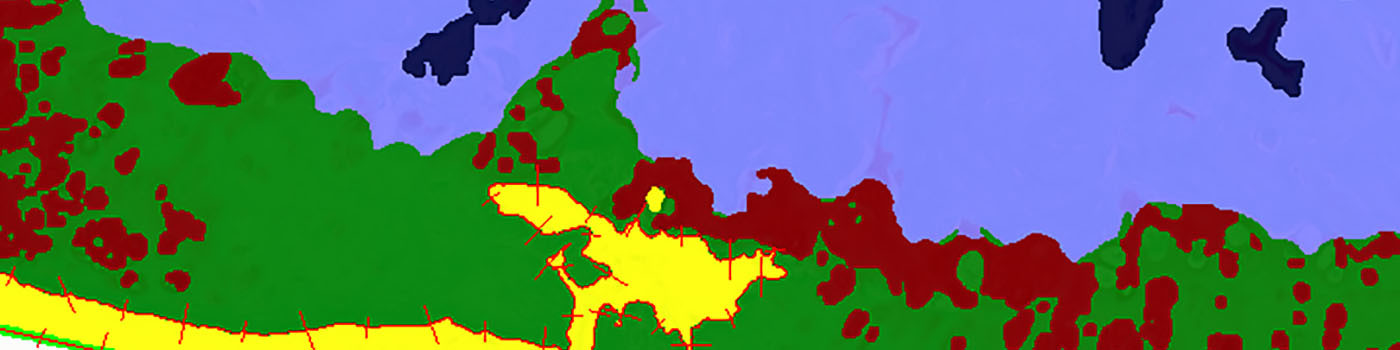
The APP will delineate the residual cartilage, the proteoglycan-stained cartilage, bone, and joint space within the Analysis Box.
On the cartilage surface towards the femur, the surface length and Euclidean length between measurement points can be obtained for calculation of the Fibrillation Index.
Due to the often weak differences in staining on bone and cartilage, and the lack of Proteoglycan stained cartilage on some sections, it is necessary to perform a review step. In the review step all images are reviewed manually, if necessary corrections are made to the tissue classification, and a calculation protocol is applied to update the results.
Staining Protocol
Execution of this APP is dependent on the standardized staining protocol ‘10027 – Rat knee joint, Saf-O-Fast Green, Joint Damage – Staining Protocol‘, developed by, Dr. Karl Rudolphi and Rolf Keiffer, Sanofi Deutschland GmbH, R&D Aging, Quality of Life.
The protocol is made available electronically upon purchase of the APP.
Keywords
Osteoarthritis, Joint, knee, Safranin-O-Fast Green, Rat, ACLT, pMx, ACLTpMx, Cartilage, Chondrocytes, Fibrillation, Bone sclerosis, quantitative, digital pathology, image analysis.
References
USERS
This APP was developed for, and validated by, Dr. Karl Rudolphi and Rolf Keiffer, Sanofi Deutschland GmbH, R&D Aging, Quality of Life.
LITERATURE
1. Gerwin, N., et. al., The OARSI histopathology initiative – recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the rat, Osteoarthritis & Cartilage 2010, 18 (S3), S24-34, DOI
2. Hayami, T., et. al., Characterization of articular cartilage and subchondral bone changes in the rat anterior cruciate ligament transection and meniscectomized models of osteoarthritis, Bone 2006, 38 (2), 234-243, DOI
3. Pritzker, K.P., et. al., Osteoarthritis cartilage histopathology: grading and staging, Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2006, 14 (1), 13-29, DOI
4. Rudolphi, K.A., et. al., Improved assessment by quantitative digital histomorphometry of histopathological changes of articular cartilage in a surgical model of post-traumatic osteoarthritis of the knee joint in rats, Osteoarthritis & Cartilage 2012, 20, S71-S128, DOI