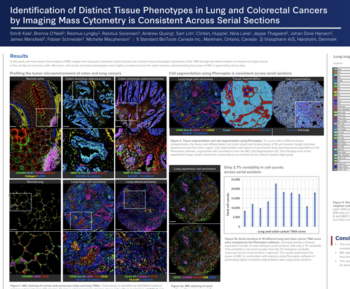
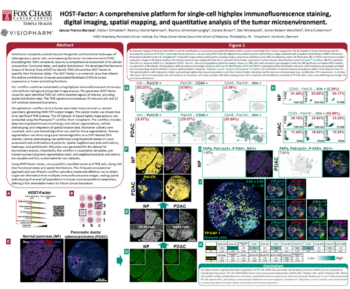
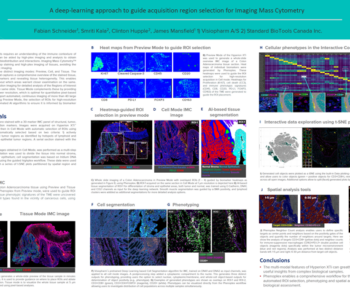
Quantitative histological analyses are used to infer pathological diagnoses and identify biological drug targets in human and laboratory animal samples. Each histological sample often include millions of cells imposing a need for automated unbiased quantitative analysis to replace manual assessment.
We have trained a convolutional neural network that can identify individual nuclei inferred from DAPI fluorescence, allowing automated quantitative analysis of various fluorescent marker levels in nuclei. We used this convolutional network to assess proliferation from nuclear Ki67 fluorescence and apoptotic DNA fragmentation from terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labelling (TUNEL) at a single cell level in human kidney biopsies. Upon retraining, the convolutional neural network was adaptable to identify nuclei from pancreas emphasizing the versatility of the network. Taken together, these results demonstrate an AI-based automated method for quantifying fluorescence levels of various markers in diverse tissues such as kidney and pancreas.

Tobias Højgaard Dovmark, Research Scientist, Novo Nordisk
As a research scientist at Novo Nordisk, I work with image analysis of histological samples. I have previously worked for Visiopharm as an image analysis specialist. I have a PhD in Physiology, Anatomy and Genetics from University of Oxford and an M.Sc. in Molecular Biomedicine from the University of Copenhagen.