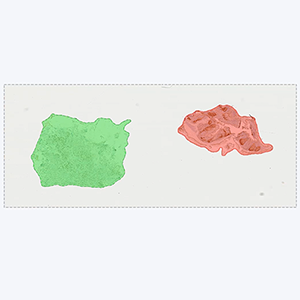
Tissue detection
Detection of sample tissue and exclusion of control tissues.
#10173
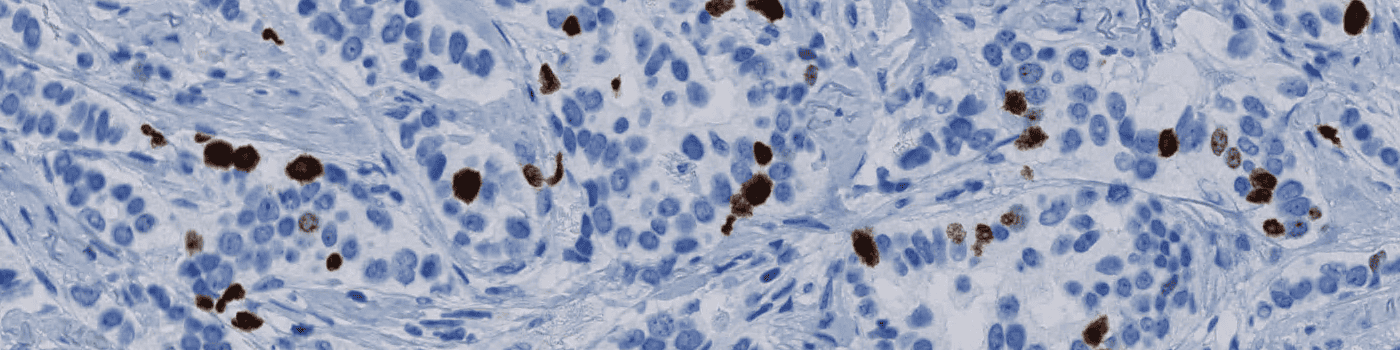
The Ki-67 protein is associated with cellular proliferation and can be assessed by Ki-67-immunohistochemical (IHC) staining.
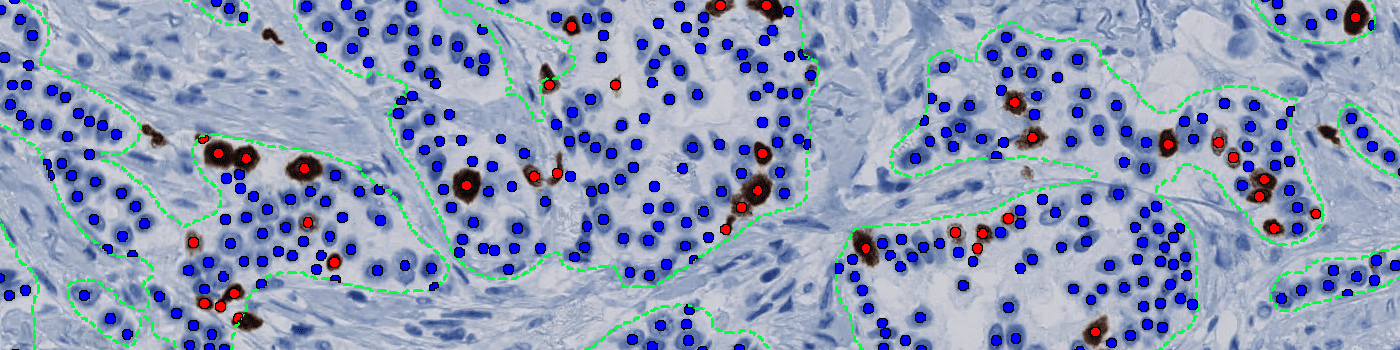
Our Ki-67 solution is fully automated and does not require manual input during analysis. The solution consists of four automated analysis steps. Once started, it automatically separates the sample tissue from control tissues and robustly identifies invasive cancer areas in the sample. Tumor nuclei are counted based on their Ki-67 expression and the resulting proliferation index for the whole tumor area is calculated.
Quantitative Output variables
The output variables obtained from this protocol are:
Workflow
Step 1: After scanning, the IMS informs the Visiopharm software about the new image and the analysis of the image is automatically started.
Alternatively, the analysis can be started manually by opening the image and starting the analysis.
Step 2: Pathologist review the analyzed image. If needed, adjustments can be made.
Additional information
Compatibility
The solution works with stains from Agilent, Roche, and Leica. It can be applied to ductal or lobular breast cancer samples.
References
1. Howard, C.V., Reed, M.G. (2005). Unbiased Stereology: Three-Dimensional Measurement in Microscopy. QTP Publications.