Breast cancer tissue stained with ER.
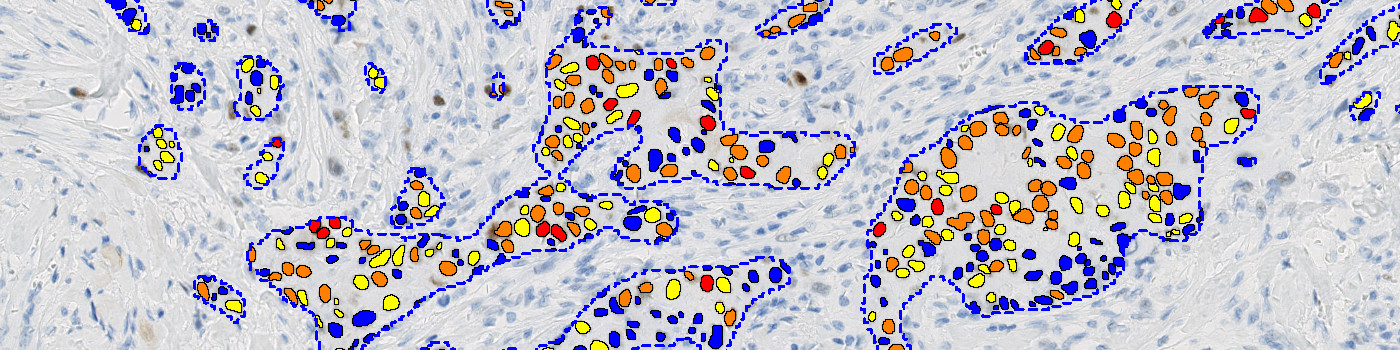
#10170
Identification and segmentation of individual nuclei in IHC images is of interest in many applications. Nuclei can be difficult to detect accurately and precisely using traditional image analysis with feature engineering. This APP utilizes artificial intelligence (AI) for automatic and robust nuclei segmentation in IHC stained tissue.
The nuclei detection performance has been assessed using precision and recall. Precision measures the ability of the APP to only detect viable nuclei and not mistake e.g. artefacts for nuclei. Recall (also known as sensitivity) measures the ability of the APP to detect all nuclei present. Precision and recall are combined to a F1-score which reflects both in a harmonic mean. Testing on 2,776 manually detected nuclei stained for ER, PR, or Ki-67, all three performance measures show excellent nuclei detection as seen from the table below.
The nuclei segmentation performance has been assessed using aggregated Jaccard index (AJI) [1] which captures the segmentation quality. Testing on 2,776 manually segmented nuclei, the performance measure shows excellent nuclei segmentation as seen from the table below.
| Precision | Recall (Sensitivity) | F1-score | AJI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 95.4 % | 95.9 % | 0.957 | 0.804 |
With an accurate nuclei segmentation, the APP can be configured to fulfill the needs of the user with Visiopharm’s Author™ module. The APP currently has two configuration options which can be switched on and off as needed:
It is also possible for the user to customize the APP by adding post-processing steps and/or output variables.
Quantitative Output variables
The APP can output the following variables:
Workflow
Step 1: Load an IHC image
Step 2: Outline tumor either manually or automatically using one of Visiopharm’s solutions
Step 3: Load and run the APP “10170 – IHC, Nuclei Detection, AI”
Methods
The APP uses a deep learning network, which has been trained using 13,434 annotated nuclei from IHC stained breast cancer tissue (ER, PR, and Ki-67), to segment nuclei. The architectural structure of the network is a U-Net which is popular for medical image segmentation. The neural network uses a cascade of layers of nonlinear processing units for feature extraction and transformation, with each successive layer using the output from the previous layers as input. U-Net uses an encoder-decoder structure with a contracting path and an expansive path. For more information on the network architecture, see [2].
Keywords
Immunohistochemistry, IHC, Nuclei Segmentation, Nuclei Detection, Artificial Intelligence, AI, Digital Pathology
References
LITERATURE
1. Kumar, N., et al. A Dataset and a Technique for Generalized Nuclear Segmentation for Computational Pathology, IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2017, 36 (17), 1550-1560, DOI
2. Ronneberger, O., et al. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation, International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, 2015, 234-241, DOI