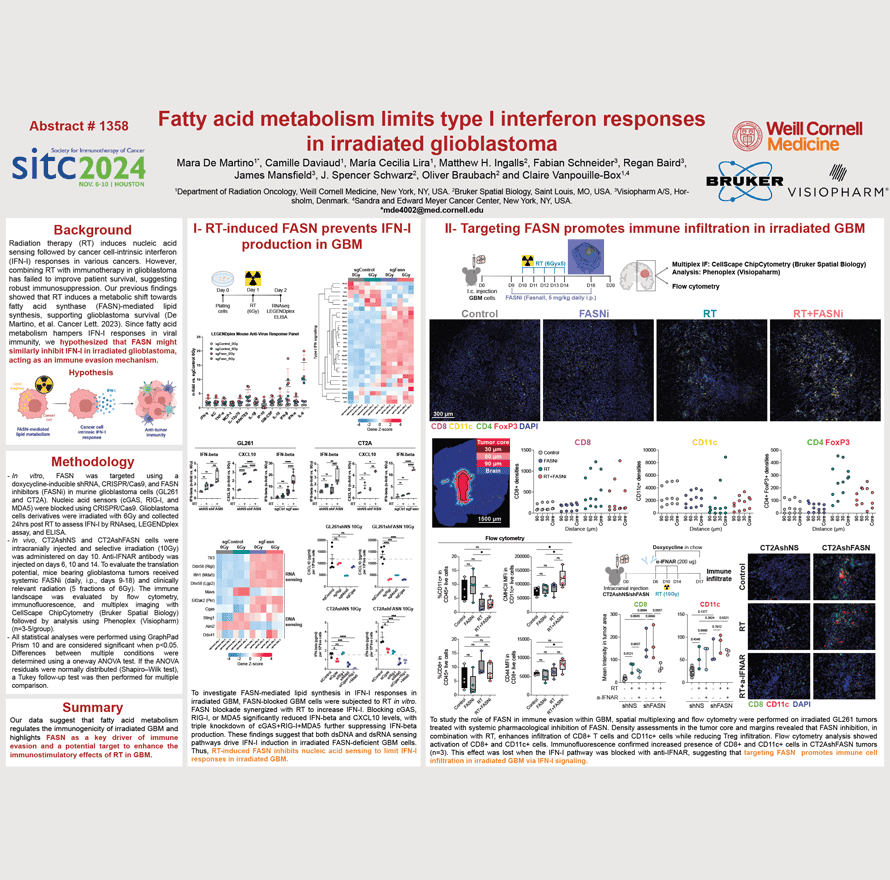
Radiation therapy (RT) induces nucleic acid sensing followed by cancer cell-intrinsic interferon (IFN-I) responses in various cancers. However, combining RT with immunotherapy in glioblastoma has failed to improve patient survival, suggesting robust immunosuppression. Our previous findings showed that RT induces a metabolic shift towards fatty acid synthase (FASN)-mediated lipid synthesis, supporting glioblastoma survival (De Martino, et al. Cancer Lett. 2023). Since fatty acid metabolism hampers IFN-I responses in viral immunity, we hypothesized that FASN might similarly inhibit IFN-I in irradiated glioblastoma, acting as an immune evasion mechanism.
Mara De Martino1, Camille Daviaud1, María Cecilia Lira1, Matthew H. Ingalls2, Fabian Schneider3, Regan Baird3, James Mansfield3, J. Spencer Schwarz2, Oliver Braubach2 and Claire Vanpouille-Box1,4
- Department of Radiation Oncology, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, USA
- Bruker Spatial Biology, Saint Louis, MO, USA
- Visiopharm A/S, Horsholm, Denmark
- Sandra and Edward Meyer Cancer Center, New York, NY, USA