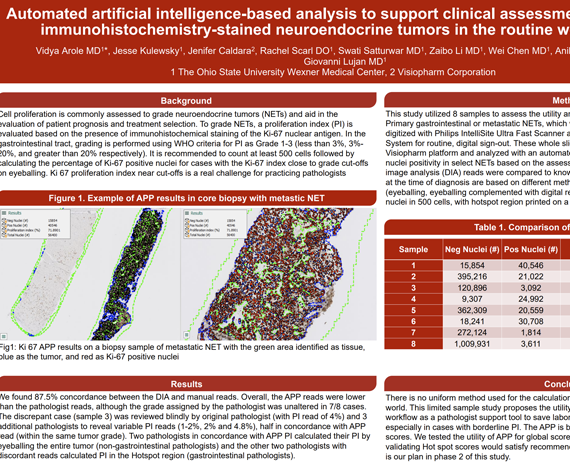

Cell proliferation is commonly assessed to grade neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) and aid in the evaluation of patient prognosis and treatment selection. To grade NETs, a proliferation index (PI) is evaluated based on the presence of immunohistochemical staining of the Ki-67 nuclear antigen. In the gastrointestinal tract, grading is performed using WHO criteria for PI as Grade 1-3 (less than 3%, 3%-20%, and greater than 20% respectively). It is recommended to count at least 500 cells followed by calculating the percentage of Ki-67 positive nuclei for cases with the Ki-67 index close to grade cut-offs on eyeballing. Ki 67 proliferation index near cut-offs is a real challenge for practicing pathologists.
Vidya Arole MD1*, Jesse Kulewsky1, Jenifer Caldara2, Rachel Scarl DO1, Swati Satturwar MD1, Zaibo Li MD1, Wei Chen MD1, Anil Parwani MD1, Giovanni Lujan MD1
- The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center
- Visiopharm Corporation