Raw image. Dermis is predominant with epidermis only as a crust of the dermis in the lower part of the image.
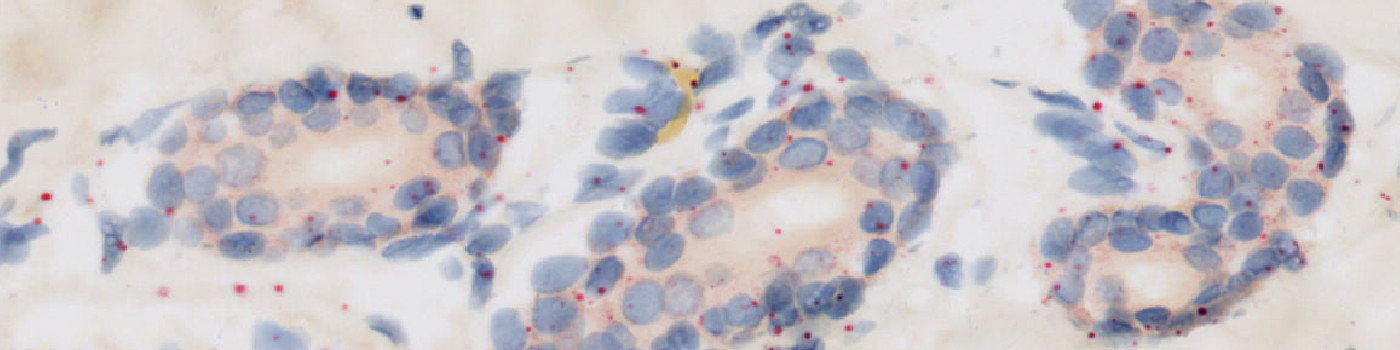

#10099
Presented in 2012, the RNAscope is one of the more recent RNA in situ hybridization techniques that allows visualization of multiple target genes. RNAscope uses a probe design strategy that amplifies the signal and suppresses the background, which results in increased sensitivity and specificity, see [1].
The protocol automatically detects and quantifies probes associated with a cell nucleus in dermis and epidermis, respectively. No manual outlining of dermis and epidermis is needed, since these regions are automatically identified.
Auxiliary APPs
ROI detection:
APP: “01 Detect ROI”
The auxiliary APP ’01 Detect ROI’ is used to automatically outline and separate the dermis and epidermis regions of interests for the subsequent analysis.
Quantitative Output variables
The output variables obtained from this protocol include:
Workflow
Step 1: Load the auxiliary APP for ROI identification: “01 Detect ROI”.
Step 2: Load the APP for identification and scoring of probes and nuclei in dermis and epidermis: “02 Analyze”.
Methods
The first image processing step involves an automated detection of the dermis and epidermis, i.e. the regions of interest (ROI) (see FIGURE 2). The nuclei and probes are subsequently detected inside these ROIs (see FIGURE 3, 5 and 7). A polynomial blob filter that enhances the probes’ features is used for the identification of the probes, whereas the haematoxylin color-deconvolution band is used for the identification of nuclei. The initial classification of nuclei and probes is managed with a postprocessing protocol to firstly refine the detection of nuclei and probes, and secondly to qualitatively determine if probes are covered by nuclei or not for the final probe quantification. For each tissue type, i.e. dermis and epidermis, probes are counted and categorized as either covered by nuclei or as separate from nuclei.
Staining Protocol
There is no staining protocol available.
Keywords
RNAscope, dermis, epidermis, skin cancer, digital pathology, image analysis.
References
LITERATURE
1. Wang, F., Flanagan, J. et. al. RNAscope – A Novel in Situ RNA Analysis Platform for Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissues, Journal of Molecular Diagnostics 2012, 14 (1), 22-29, DOI.