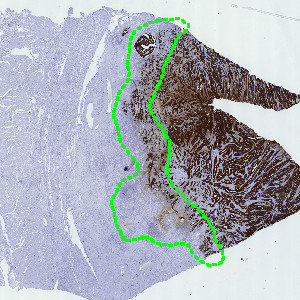
Colon tissue where the invasive front of colorectal cancer is manually marked (green ROI).
#10117
Tumor budding refers to the presence of individual or small clusters of tumor cells (tumor buds) at the invasive front of carcinomas. Particularly in the setting of colorectal carcinoma, tumor budding has been pointed out as a strong and reproducible prognostic factor, dividing patients into risk categories with a different perspective than TNM staging, see [1].
This protocol can be used to quantify tumor budding in PCK stained colorectal sections. The APP detects tumor buds in a manually marked invasive front and assigns hot spots to the ten most affected areas.
Quantitative Output variables
The output variables obtained from this protocol are:
Workflow
WORKFLOW
Step 1: Manually outline the invasive front as the region of interest (ROI) (see FIGURE 1).
Step 2: Load and run the APP for elimination of large structures “01 Eliminate Large Structures”.
Step 3: Load and run the APP for tumor bud detection “02 Detect Tumor Buds”.
Step 4: Load and run the APP for finding the ten areas with the most tumor buds “03 Detect Hotspots”
Step 5: Load the quantification protocol “04 Quantify”. Click the save button to transfer the results to the database.
Methods
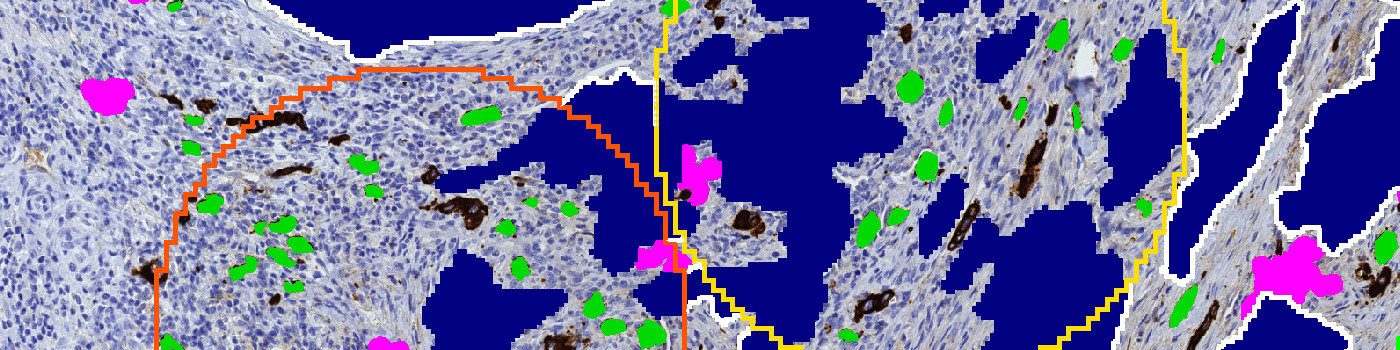
Within the manually marked invasive front the first processing step identifies and excludes PCK positive structures that are too large to be characterized as tumor buds. The next step involves a detection of the tumor buds based on the size and shape of the remaining PCK positive structures within the invasive front. Structures, that based on shape and size could have been tumor buds, but that show weak affinity for PCK are characterized as diffuse areas. Finally, a heatmap based on the number of tumor buds is created and used for localization of the ten hottest hot spots. The hot spots are color coded for easy visualization of the hottest hot spot (color scale: blue – red, red being the hottest).
Staining Protocol
There is no staining protocol available.
Keywords
Colorectal cancer, tumor budding, hot spot, invasive front, PCK, cytokeratin, IHC, immunohistochemistry, digital pathology, image analysis, tumor progression
References
LITERATURE
1. Mitrovic, B. et. al. Tumor budding in colorectal carcinoma: time to take notice, Modern Pathology 2012, 25 (10), 1315-1325, DOI.