CK5 stained slide.
#10096
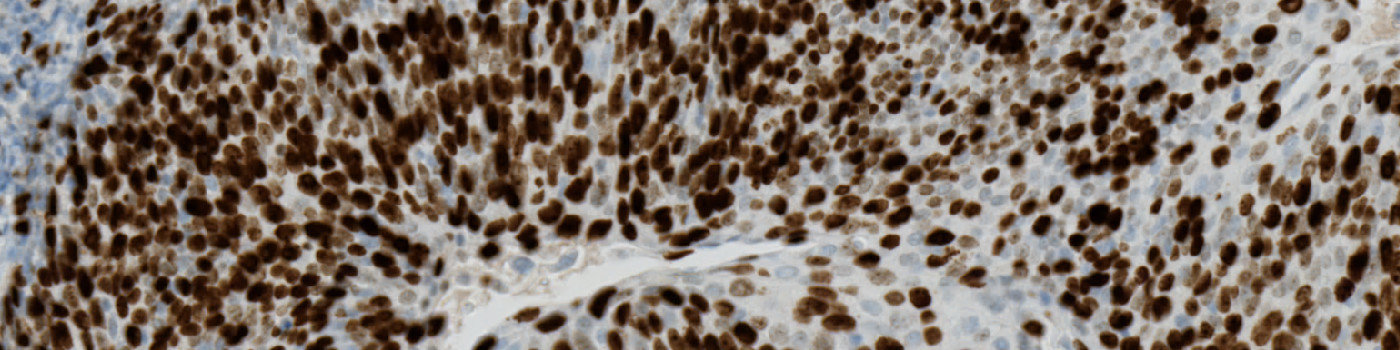
The Ki-67 protein is associated with cellular proliferation, and the protein is present in the nucleus of all cells that are in the active phase of the cell cycle, but absent in resting cells, see [1]. The cell proliferation rate can be assessed by Ki-67-immunohistochemical (IHC) staining, and this can be correlated to the tumor grade and the clinical course, see [2].
This protocol can be used to assess tumors by determining the Ki-67 positivity.
Two serial sections stained for Ki-67 and CK5, respectively, must be used in this APP. Tumor regions are identified automatically on the CK5 stained slides using the VirtualDoubleStaining™ technique, and the outlined tumor regions are overlaid on the Ki-67 stained slide, thus automatically identifying tumor regions.
Auxiliary APPs
APP: “01 Tumor Detection”
The auxiliary APP ’01 Tumor Detection” is used for automatic tumor detection.
Quantitative Output variables
The output variables obtained from this protocol include:
Workflow
Step 1: Load the auxiliary APP for tumor region identification: “01 Tumor Detection”.
Step 2: Load the APP for identification and scoring of Ki-67 stained cells: “02 Analyze”.
Methods
The Ki-67 and CK5 serial sections are linked together and aligned via the Tissuealign™ workflow that allows for an easy user-assisted computational alignment.
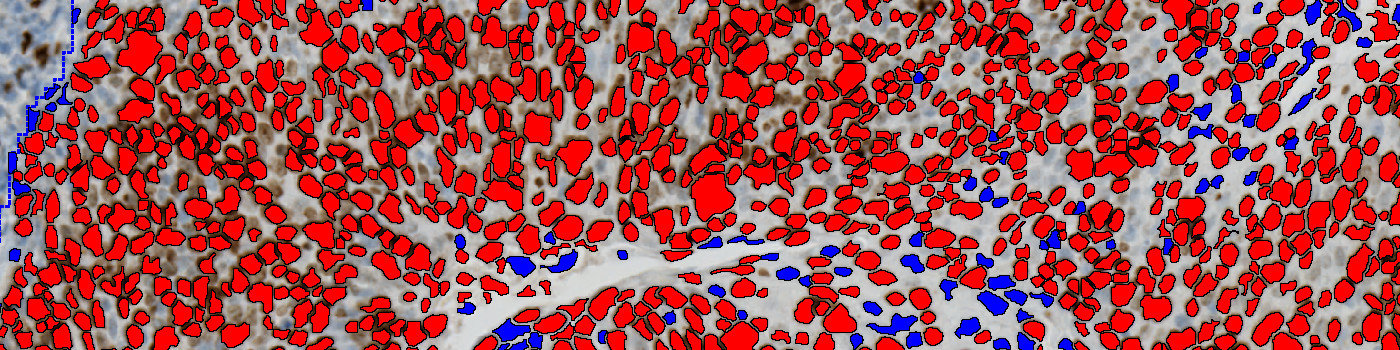
Tumor areas are automatically detected from the CK5 slide and outlined as regions of interest (ROIs). The ROIs are superimposed onto the aligned Ki-67 tissue slide to outline the tumor region on the Ki-67 slide. The subsequent analysis is now limited to the inside of the tumor regions only.
Ki-67 negative and positive nuclei are detected and delineated from their surroundings to accurately quantify nuclei in highly concentrated areas.
Staining Protocol
There is no staining protocol available.
Keywords
Ki-67, CK5, proliferation, VirtualDoubleStaining™, VDS™, neck, throat, immunohistochemistry, quantitative, digital pathology, image analysis.
References