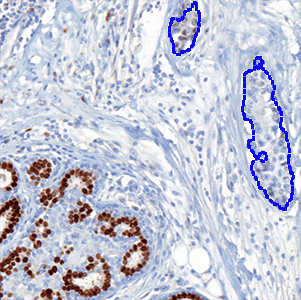
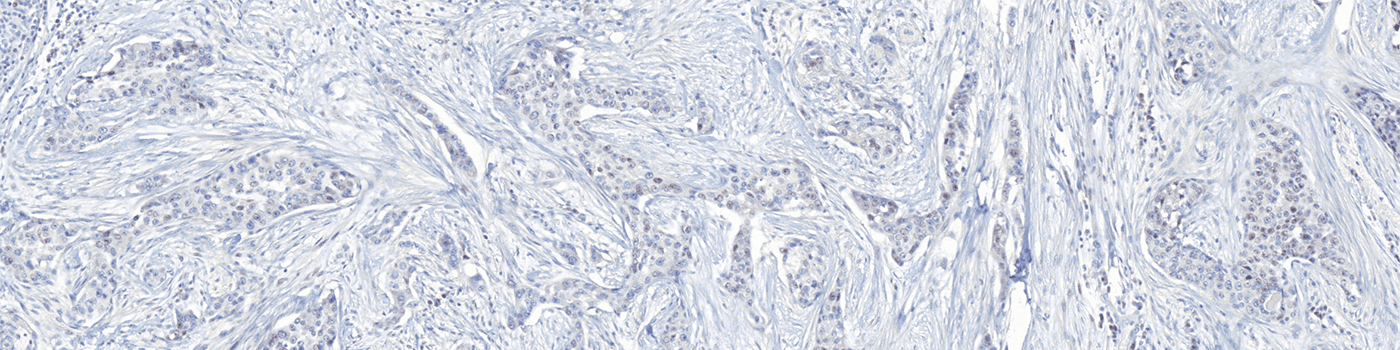
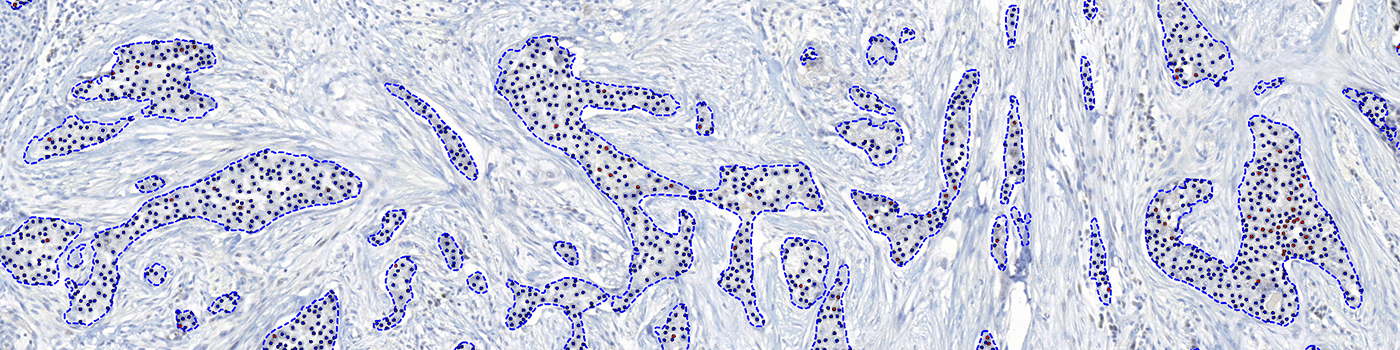
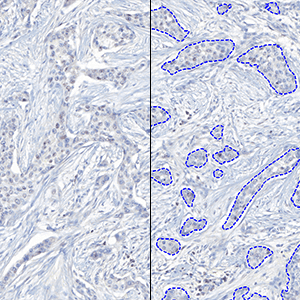
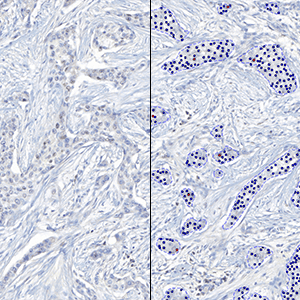
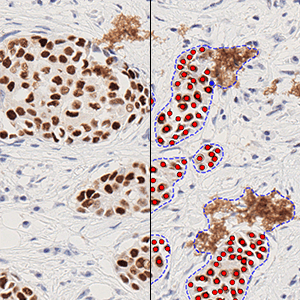
The outputs of the device are:
Total Nuclei [#],
which is the total count of detected nuclei in all invasive tissue
Positive Nuclei [%],
which is a value between 0 and 100 and is calculated as
Positive Nuclei [%] = (Number of ER positive nuclei)/(Total number of nuclei) × 100
An optional output is the
Allred Score,
which is a value between 0 and 8 and is calculated as
Allred Score = Proportion Score + Intensity Score
where Proportion Score is a value between 0 and 5 which reflects the positive percentage, and Intensity Score is a value between 0 and 3 which reflects the intensity of the ER positive nuclei.