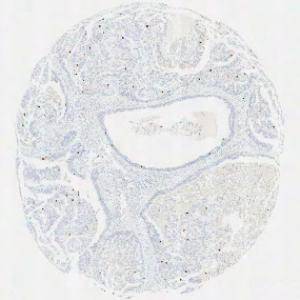
Original TMA-core stained with PHH3.
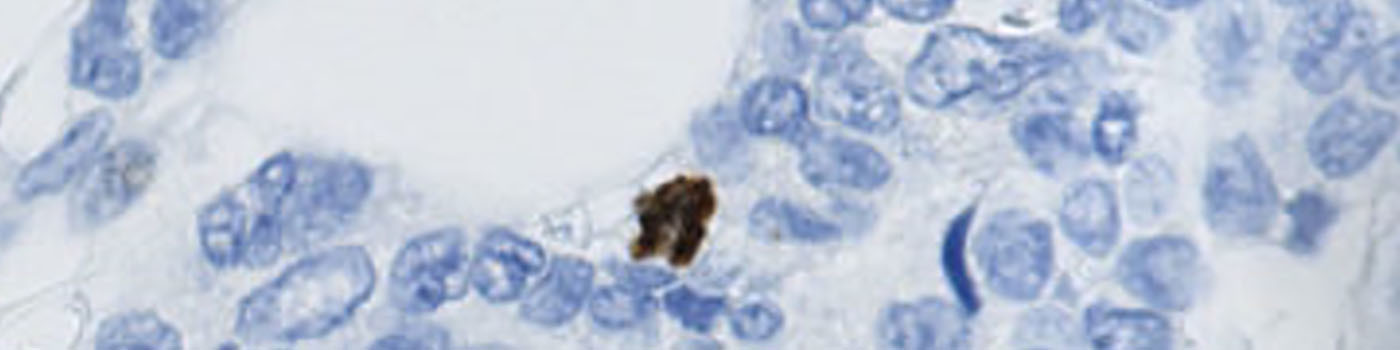
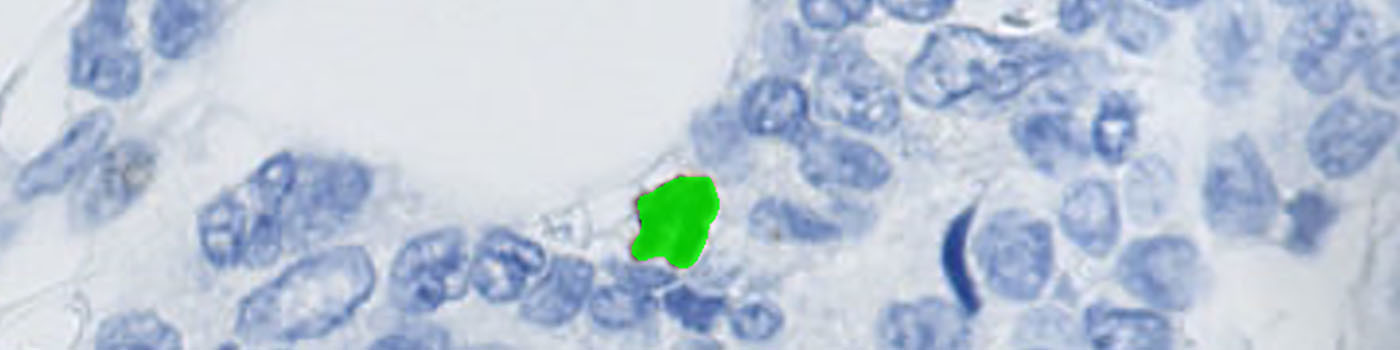
#10048
This APP has been developed to quantify the mitotic index of PHH3 positive cells within breast carcinoma. Phosphohistone H3 (PHH3) is a mitotic marker and has prognostic capabilities when applied to breast cancer tissue, see [3]. The mitotic index can be obtained by PHH3-immunohistochemical staining, which can be used as a supplement for diagnosis.
Quantitative Output variables
The output variables obtained from this protocol include the number of positive nuclei profiles, the area of tumor tissue and the mitotic index. The mitotic index is calculated as follows:
Methods
Tumor areas are manually outlined as regions of interest (ROIs) (see FIGURE 2). The ROIs are used for subsequent analysis limited to the inside of the tumor regions (see FIGURE 3).
Segmentation is performed of all nuclei (both PHH3 positive and negative). The method for nuclei separation which is based on shape, size and nuclei probability is used, employing a fully automated watershed-based nuclei segmentation technique. A post-processing step involving a morphological closing operation is applied to avoid counting nuclei in the late mitotic phase (anaphase and telophase) as two nuclei.
The number of positive PHH3 nuclei and the mitotic index is calculated.
Keywords
Breast carcinoma, PHH3, Phosphohistone, immunohistochemistry, breast cancer, quantitative, digital pathology, image analysis, mitotic index, TMA
References
LITERATURE
1. Skaland, I., et. al. Phosphohistone H3 expression has much stronger prognostic value than classical prognosticators in invasive lymph node-negative breast cancer patients less than 55 years of age, Mod Pathol 2007, 20 (12), 1307-15, DOI
2. Kårsnäs, A., et. al., Learning histopathological patterns, Journal of Pathology Informatics, 2011, 2 (2), S12, DOI
3. Jung, C., et. al., Segmenting Clustered Nuclei Using H-minima Transform-Based Marker Extraction and Contour Parameterization, IEEE Transactions on Bio-medical Engineering, 2010, 57 (10), 2600-4, DOI